Search Results
-
-
-
-
The Baden-Württemberg healthcare industry https://www.gesundheitsindustrie-bw.de/en/location/start-upCompany foundation
-
-
The Baden-Württemberg healthcare industry https://www.gesundheitsindustrie-bw.de/en/facts-and-figuresAt a glance
-
The Baden-Württemberg healthcare industry https://www.gesundheitsindustrie-bw.de/en/location/pharmaThe pharmaceutical industry
-
The Baden-Württemberg healthcare industry https://www.gesundheitsindustrie-bw.de/en/location/medtechMedical technology
-
The Baden-Württemberg healthcare industry https://www.gesundheitsindustrie-bw.de/en/location/biotechThe biotechnology sector
-
-
Dossier - 13/04/2015 
Boosting the immune system can improve cancer prevention and treatment
The activation of the body’s immune system to fight cancer is not only a promising therapeutic concept, but is already used in medical practice. The first immunotherapies have been approved and many more are either in the experimental stages or already undergoing clinical testing. Vaccines to prevent certain types of cancer are already being used successfully around the world.
https://www.gesundheitsindustrie-bw.de/en/article/dossier/boosting-the-immune-system-can-improve-cancer-prevention-and-treatment -
Dossier - 09/03/2015 
Advances in the study and treatment of liver diseases
Liver diseases are often underestimated despite being quite common and potentially having serious and even life-threatening consequences, especially in chronic cases. The most common causes of liver diseases are hepatitis viruses, excessive alcohol consumption, and obesity; congenital or autoimmune liver diseases are quite rare. Thanks to advances in medical research, diseases such as hepatitis B and C can be treated effectively.
https://www.gesundheitsindustrie-bw.de/en/article/dossier/advances-in-the-study-and-treatment-of-liver-diseases -
Dossier - 09/02/2015 
Chemical tools for biological applications
The boundaries between traditional scientific disciplines are becoming less and less distinct. Interdisciplinary cooperation is often required to study complex processes and biomolecular issues. Interdisciplinary cooperation is central to chemical biology.
https://www.gesundheitsindustrie-bw.de/en/article/dossier/chemical-tools-for-biological-applications -
Dossier - 10/11/2014 
Cell and gene therapies from bench to bedside
While cell therapy has become standard treatment for a number of blood cancers, most cell and gene therapy approaches for the treatment of hereditary and metabolic diseases, neurodegenerative disorders and cancer are still in the experimental phases or early clinical trials. However, recent successes give rise to the hope that cell and gene therapies will in future make important contributions to previously incurable diseases.
https://www.gesundheitsindustrie-bw.de/en/article/dossier/cell-and-gene-therapies-from-bench-to-bedside -
Dossier - 30/06/2014 
Addiction new concepts for resolving old problems
Addictive substances and behaviours are as varied as their effects on an addict’s health and personality. However, modern neurobiological research has revealed common principles in the development and continuation of addiction, which can be used as an approach for new prevention and therapy strategies including the prevention of relapses. This dossier presents some of the latest research results in the field.
https://www.gesundheitsindustrie-bw.de/en/article/dossier/addiction-new-concepts-for-resolving-old-problems -
Dossier - 16/06/2014 
Biotechnology as a tool for the production of food
Biotechnology opens up numerous opportunities for the food industry. The targeted use of biotechnological methods can help reduce the quantity and number of unhealthy ingredients in foods as well as degrade allergenic substances. Genomic research and targeted breeding also greatly facilitate progress in agriculture. Food biotechnology therefore contributes significantly to saving resources, optimising harvest yields and producing better foods.
https://www.gesundheitsindustrie-bw.de/en/article/dossier/biotechnology-as-a-tool-for-the-production-of-food -
Dossier - 02/06/2014 
Bioanalysis techniques for the characterization of biological material
Science constantly provides researchers with new challenges biologists and bioanalysts have to deal with and which come from sources as varied as the ever increasing number of resistant pathogenic bacterial strains or the famine conditions in Third-World countries. In the search for scientific truths bioanalysis is the development optimization and application of the entire range of analytical methods available. However we need to keep in mind…
https://www.gesundheitsindustrie-bw.de/en/article/dossier/bioanalysis-techniques-for-the-characterization-of-biological-material -
Dossier - 28/04/2014 
Data mining new opportunities for medicine and public health
Research and healthcare activities produce huge quantities of data that need to be presented in an understandable structure. This requires computer-assisted extraction of relevant data and the use of statistical methods. This process, known as data mining, enables the discovery of patterns in large data sets. Data mining methods are of particular importance in fields that use high-throughput, visualisation methods and telemedical applications.
https://www.gesundheitsindustrie-bw.de/en/article/dossier/data-mining-new-opportunities-for-medicine-and-public-health -
Dossier - 31/03/2014 
Peptides diverse molecules of life
Peptides exist in all organisms, wherever there are cells. The range of their physiological functions is huge. Biologically active peptides can act as hormones, neurotransmitters, growth factors as well as toxins and antibiotics. This is what makes them highly interesting drug leads. They are used for the treatment of autoimmune diseases, cancer and other diseases. Peptides are gaining in importance as candidates for drugs.
https://www.gesundheitsindustrie-bw.de/en/article/dossier/peptides-diverse-molecules-of-life -
Dossier - 10/03/2014 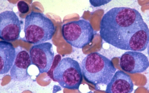
Cancer therapy and cancer diagnostics
Thanks to improved diagnostics and therapy, today’s cancer patients can live considerably longer than patients several years ago. Nevertheless, some cancers, especially the strongly metastatic ones, are difficult to treat. Therapies targeting immune cells or cancer stem cells could potentially improve the current situation.
https://www.gesundheitsindustrie-bw.de/en/article/dossier/cancer-therapy-and-cancer-diagnostics -
Dossier - 10/02/2014 
Multiresistant pathogens a self-inflicted threat?
Most bacterial infections have lost their capacity to cause terror thanks to antibiotics. However, the increase in antibiotic resistances is making the fight against bacterial pathogens rather difficult, and the widespread overuse and inappropriate use of antibiotics continues to fuel the increase in antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
https://www.gesundheitsindustrie-bw.de/en/article/dossier/multiresistant-pathogens-a-self-inflicted-threat -
Dossier - 20/01/2014 
Optogenetics switching cell activity on and off with light
What still sounds like science fiction to the general public has long been within reach for many years scientists have been able to manipulate neural activity selectively with light. They use different wavelengths to turn cells on and off as if they were a standard switch. Optogenetics is an emerging technology that combines optics and genetics. The technology is already used in many different ways for many different purposes by numerous research…
https://www.gesundheitsindustrie-bw.de/en/article/dossier/optogenetics-switching-cell-activity-on-and-off-with-light -
Dossier - 02/12/2013 
RNA interference confidence is returning
The 15-year history of RNA interference is not short on dramatic effects. It begins with the unexpected discovery and publication of the process of post-transcriptional gene silencing in 1998 for which Andrew Fire and Craig Mello were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine just eight years after their discovery. In 2001 Thomas Tuschl succeeded in switching off genes in human cells with small synthetic pieces of RNA siRNA.
https://www.gesundheitsindustrie-bw.de/en/article/dossier/rna-interference-confidence-is-returning